The Eight Auspicious Signs of Tibetan Buddhism
The Eight Auspicious Signs (also knows as Ashtamangalas) is a sacred suite of symbols, endemic to a number of religions, such as Buddhism and Hinduism.
These symbols or “symbolic attributes” point to qualities of enlightened mindstream, and are the investiture that ornaments these enlightened “qualities”.
Groupings of eight auspicious symbols were originally used in India at ceremonies such as an investiture or coronation of a king. In Buddhism, these eight symbols of good fortune represent the offerings made by the gods to Siddharta Gautama immediately after he gained enlightenment.
The Eight Auspicious Signs / symbols are
The Conch

he right-turning white conch / shell represents the beautiful, deep, melodious, interpenetrating and pervasive sound of the dharma, which awakens disciples from the deep slumber of ignorance and urges them to accomplish their own welfare for the welfare of others.
The Indian god Vishnu is described as having a conch shell as one of his main emblems: his shell bore the name Panchajanya meaning “having control over the five classes of beings”.
The Endless knot

It is a symbol of the ultimate unity of everything. Moreover, it represents the intertwining of wisdom and compassion, the mutual dependence of wisdom and method, the inseparability of wisdom and compassion.
Pair of Golden Fish
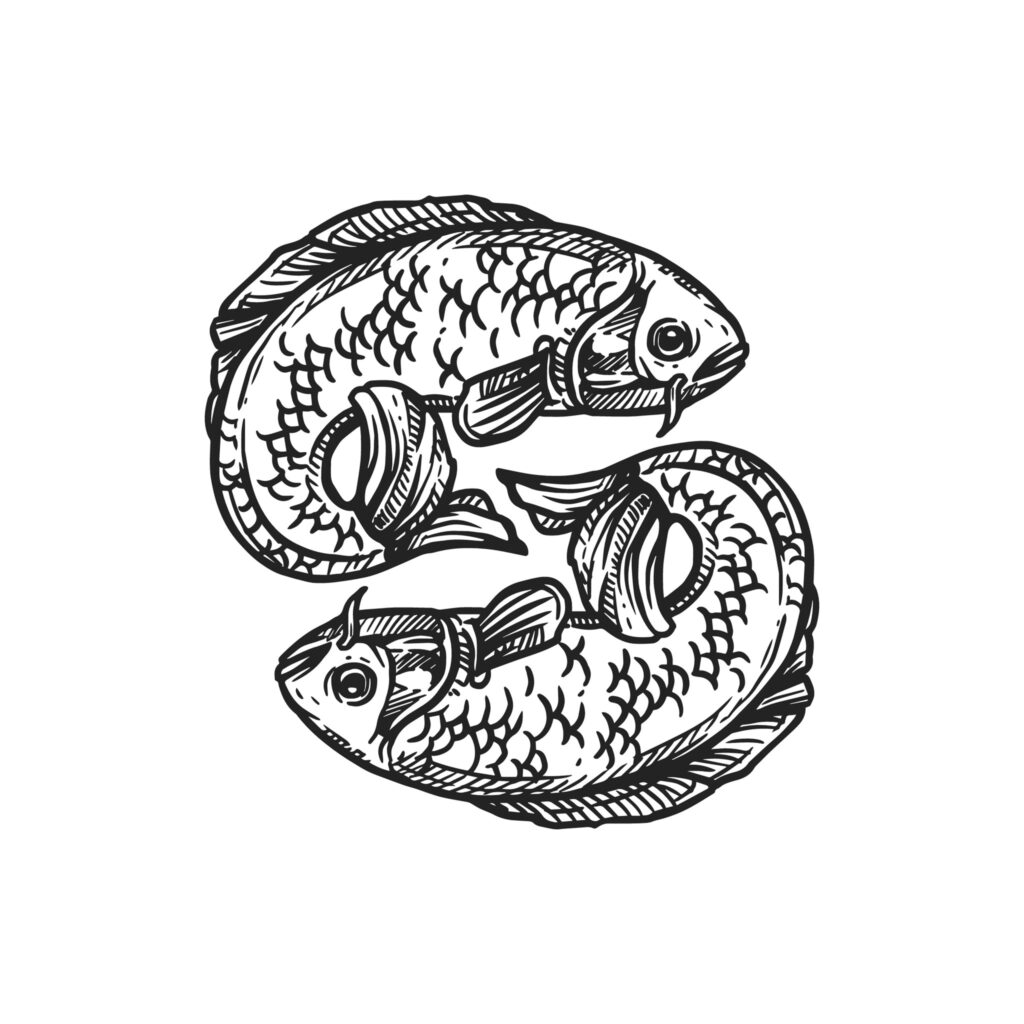
The two fishes originally represented the two main sacred rivers of India – the Ganges and Yamuna. These rivers are associated with the lunar and solar channels, which originate in the nostrils and carry the alternating rhythms of breath or prana.
In Buddhism, the fish symbolize happiness as they have complete freedom of movement in the water. They represent fertility and abundance. Often drawn in the form of carp, which are regarded in the Orient as sacred on account of their elegant beauty, size, and life-span.
Lotus
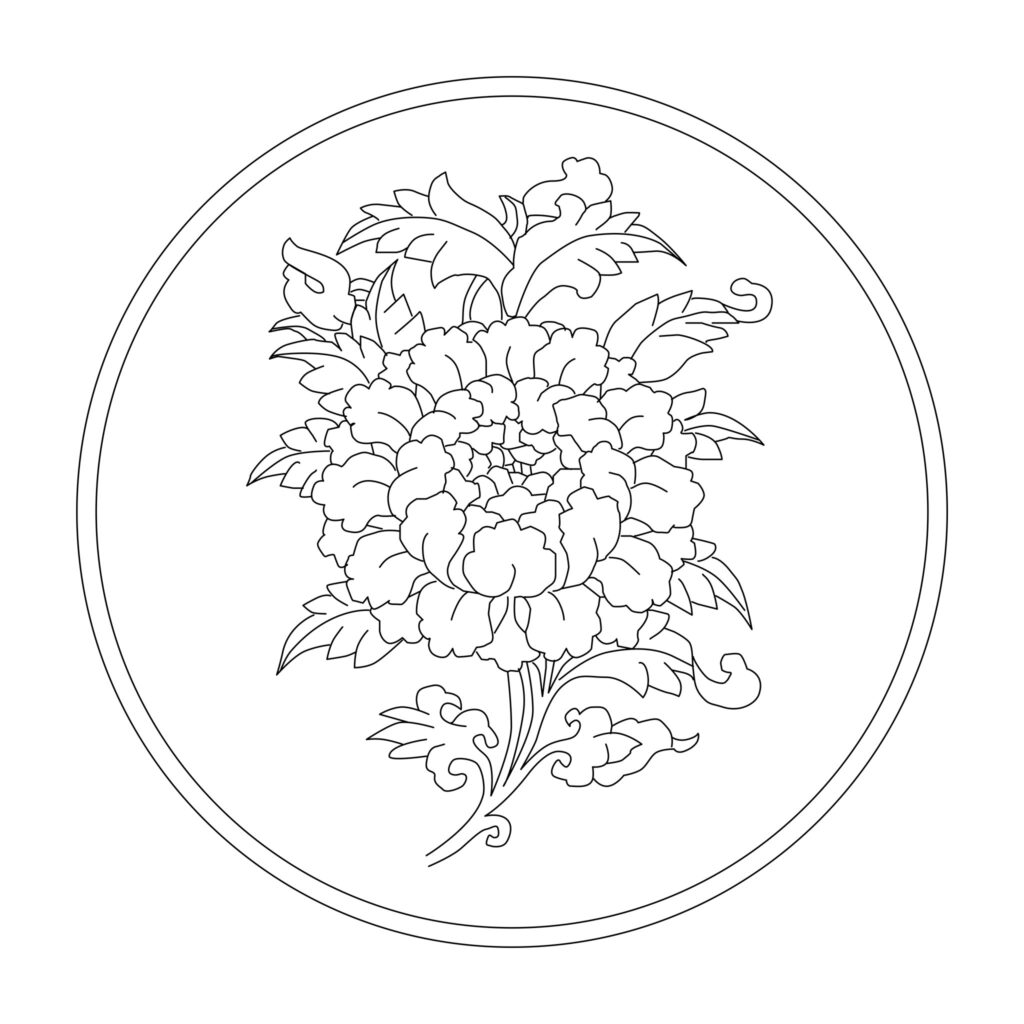

The lotus flower represent the primordial purity of body, speech, and mind, floating above the muddy waters of attachment and desire. The lotus symbolizes purity and renunciation. Although the lotus has its roots in the mud at the bottom of a pond, its flower lies immaculate above the water. The Buddhist lotus bloom has 4, 8, 16, 24, 32, 64, 100, or 1,000 petals.
Parasol

The jewelled parasol represents the protection of beings from harmful forces and illness. It represents the canopy or the sky and therefore the expansiveness and unfolding of space and the element æther. It represents the expansiveness, unfolding and protective quality of the sahasrara: the “thousand-petalled”, crown chakra, considered the seventh primary chakra.
Vase
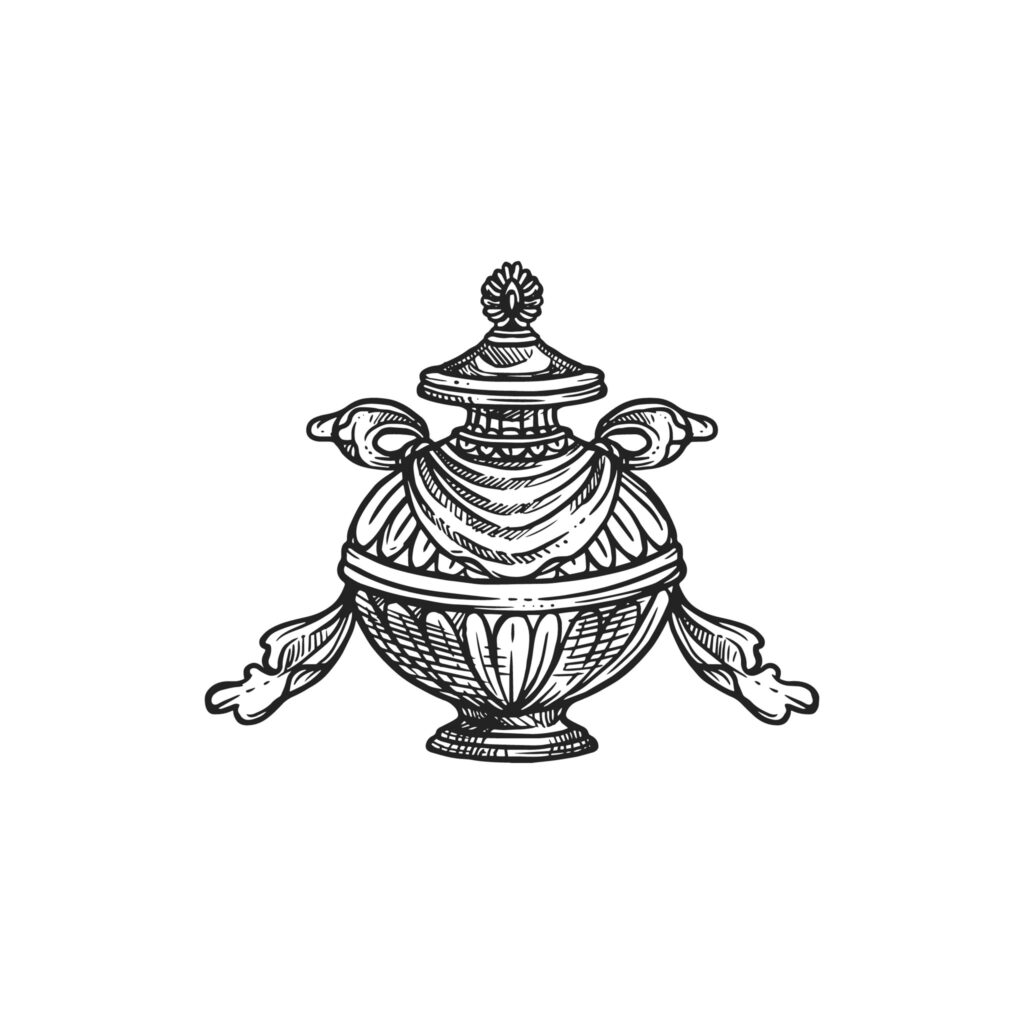

The Treasure vase represents health, longevity, wealth, prosperity, wisdom and the phenomenon of space. The treasure vase, or pot, symbolizes the Buddha’s infinite quality of teaching the dharma: no matter how many teachings he shared, the treasure never lessened.
Dharmachakra

The Dharmachakra, or Wheel of the Law represents Gautama Buddha and the Dharma teaching.
Victory Banner
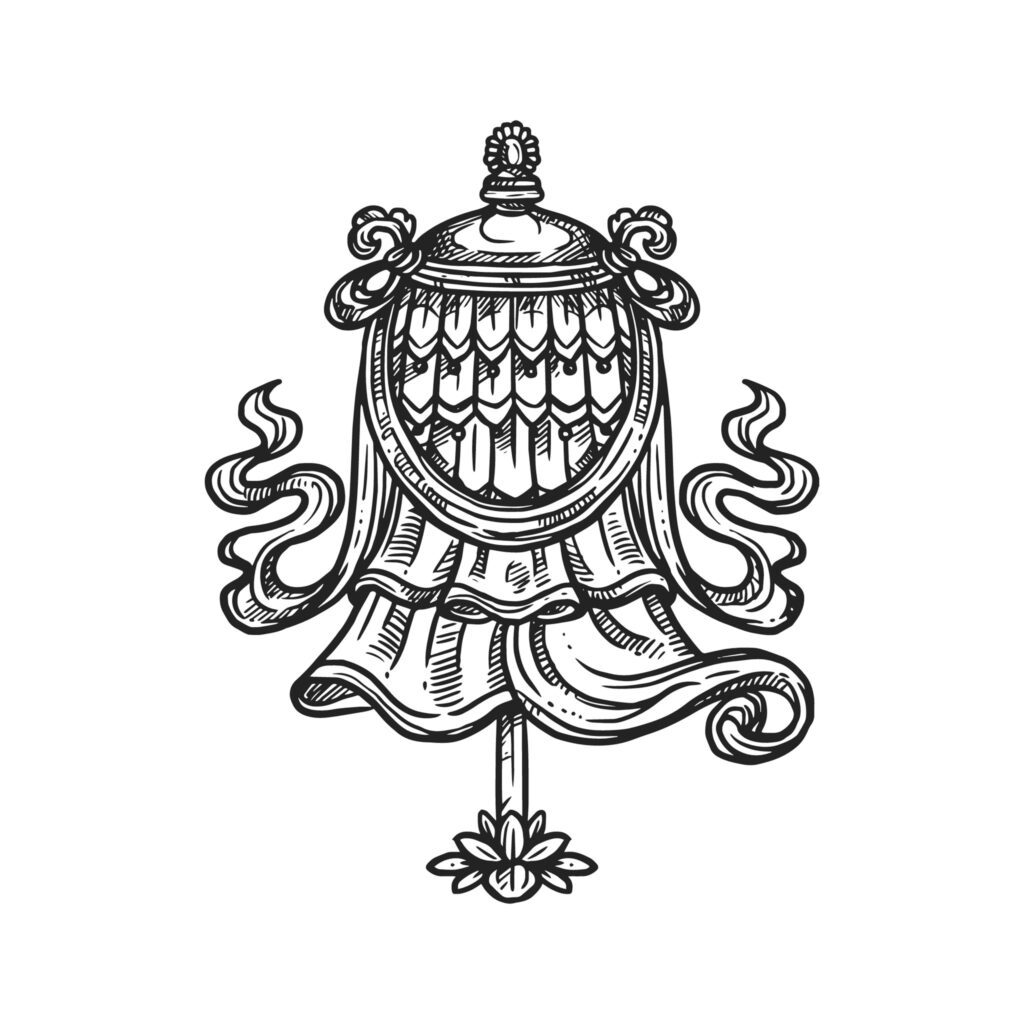
It was a military standard of ancient Indian warfare. The symbol represents the Buddha’s victory over the four maras (demons), or hindrances in the path of enlightenment. These hindrances are pride, desire, disturbing emotions, and the fear of death.
THE SEQUENCE OF THE 8 SYMBOLS
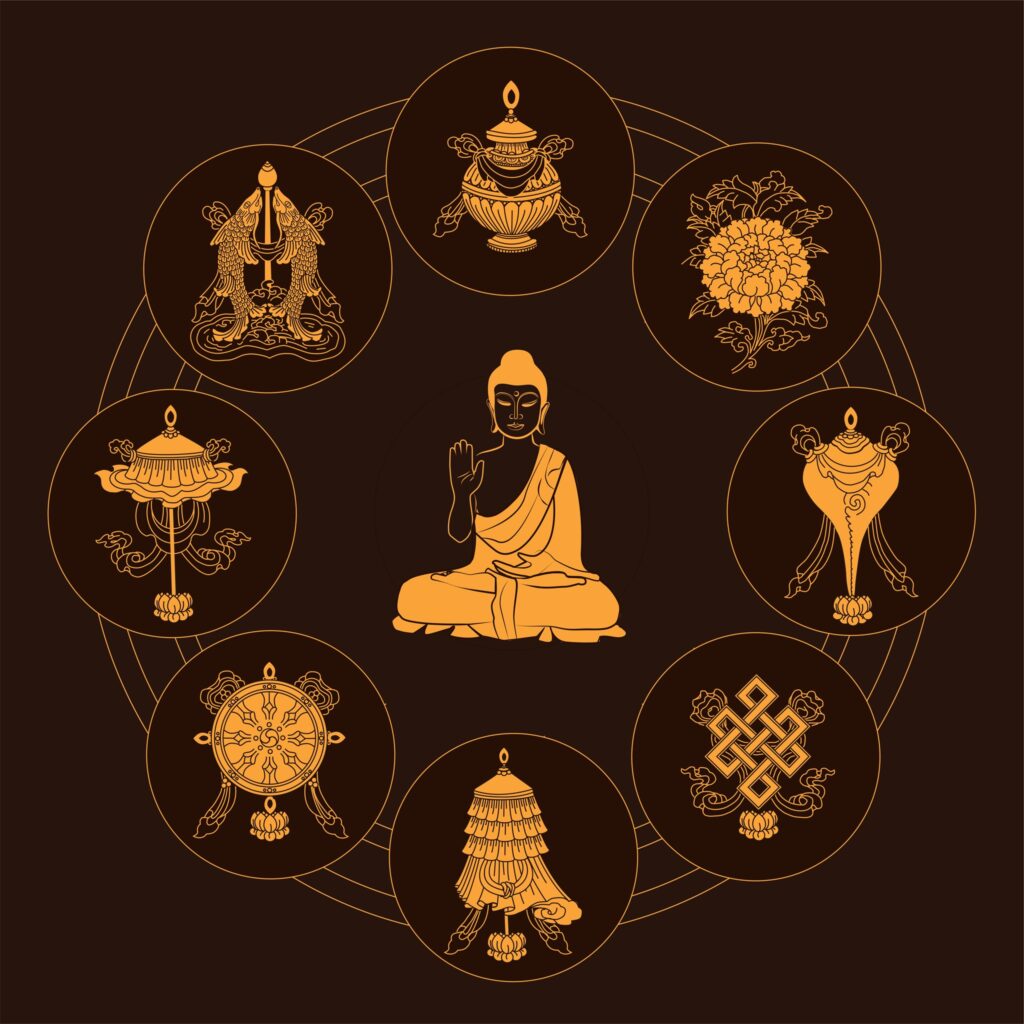

The sequential order of the Eight Auspicious Symbols in Tibetan Buddhism
- Endless knot
- Victory Banner
- Dharmachakra (fly-whisk in Nepali Buddhism)
- Parasol
- Golden Fish
- The Vase
- Lotus
- Conch








